Posts Tagged ‘software de memória flash de microprocessador bloqueado’
 Reverse ATmega8A Microchip Memory Code
Reverse ATmega8A Microchip Memory Code
Reverse ATmega8A Microchip Memory Code needs to decode atmega8a microprocessor’s tamper resistance system, then readout MCU ATmega8a firmware from its flash and eeprom memory;

There are basically two types of interrupts. The first type is triggered by an event that sets the Interrupt Flag. For these interrupts, the Program Counter is vectored to the actual Interrupt Vector in order to execute the interrupt handling routine, and hardware clears the corresponding Interrupt Flag.
Interrupt Flags can also be cleared by writing a logic one to the flag bit position(s) to be cleared. If an interrupt condition occurs while the corresponding interrupt enable bit is cleared to duplicate avr microprocessor atmega8 protected firmware, the Interrupt Flag will be set and remembered until the interrupt is enabled, or the flag is cleared by software.
Similarly, if one or more interrupt conditions occur while the global interrupt enable bit is cleared, the corresponding Interrupt Flag(s) will be set and remembered until the global interrupt enable bit is set, and will then be executed by order of priority.
The second type of interrupts will trigger as long as the interrupt condition is present. These interrupts do not nec- essarily have Interrupt Flags. If the interrupt condition disappears before the interrupt is enabled, the interrupt will not be triggered.
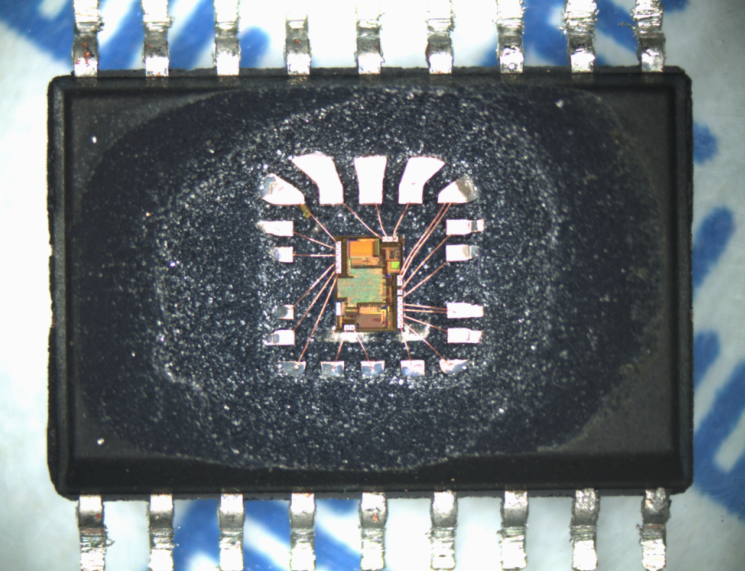
 Microcontroller ATmega8L Flash Data Restoration
Microcontroller ATmega8L Flash Data Restoration
Microcontroller ATmega8L Flash Data Restoration is a process started from clone mcu atmega8l code from its flash memory, the embedded firmware will be readout from atmega8 microprocessor;
The Stack is effectively allocated in the general data SRAM, and consequently the Stack size is only limited by the total SRAM size and the usage of the SRAM. All user programs must initialize the SP in the reset routine (before sub-routines or interrupts are executed).
The Stack Pointer SP is read/write accessible in the I/O space. The data SRAM can easily be accessed through the five different addressing modes supported in the AVR architecture when copy mcu atmega8l heximal.
The memory spaces in the AVR architecture are all linear and regular memory maps.

microcontrolador ATmega8L restauração de dados flash é um processo iniciado a partir de clone mcu atmega8l código de sua memória flash, o firmware incorporado será lido a partir do microprocessador atmega8
A flexible interrupt module has its control registers in the I/O space with an additional global interrupt enable bit in the Status Register. All interrupts have a separate Interrupt Vector in the Interrupt Vector table.
The interrupts have priority in accordance with their Interrupt Vector position. The lower the Interrupt Vector address, the higher the priority. The I/O memory space contains 64 addresses for CPU peripheral functions as Control Registers to attack microcontroller atmega8a binary, SPI, and other I/O functions . The I/O Memory can be accessed directly, or as the Data Space locations following those of the Reg- ister File, 0x20 – 0x5F.