 STMicrocontroller STM8L052C6T6 Locked Flash Memory Decryption
STMicrocontroller STM8L052C6T6 Locked Flash Memory Decryption
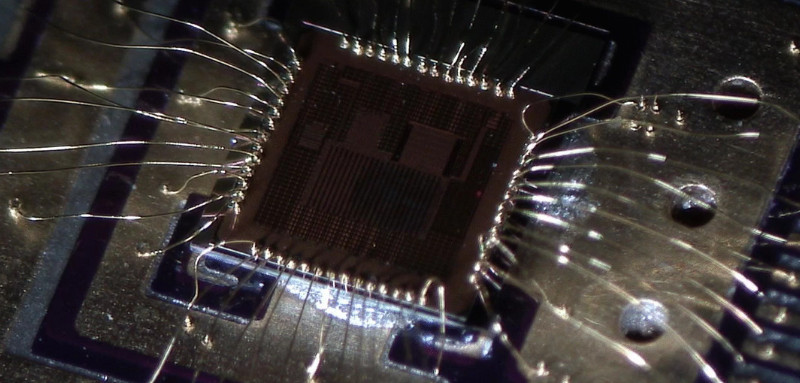
STMicrocontroller STM8L052C6T6 Locked Flash Memory Decryption refers to unlock the fuse bit of stm8l052 by focus ion beam and extract source code from stm8l052 mcu flash memory.
The high-density and medium+ density STM8L15xx6/8x devices feature a nested vectored interrupt controller:
Nested interrupts with 3 software priority levels
32 interrupt vectors with hardware priority
Up to 40 external interrupt sources on 11 vectors
Trap and reset interrupts
The device requires a 1.65 V to 3.6 V operating supply voltage (VDD). The external power supply pins must be connected as follows:
VSS1, VDD1, VSS2, VDD2, VSS3, VDD3, VSS4, VDD4= 1.65 to 3.6 V: external power supply for I/Os and for the internal regulator. Provided externally through VDD pins, the corresponding ground pin is VSS. VSS1/VSS2/VSS3/VSS4 and VDD1/VDD2/VDD3/VDD4 must not be left unconnected by restoring microcontroller stm8s103k3 embedded flash memory.
VSSA, VDDA = 1.65 to 3.6 V: external power supplies for analog peripherals (minimum voltage to be applied to VDDA is 1.8 V when the ADC1 is used). VDDA and VSSA must be connected to VDD and VSS, respectively.
VREF+, VREF- (for ADC1): external reference voltage for ADC1. Must be provided externally through VREF+ and VREF- pin in order to reverse engineer microcontroller stm8s105k6 structure.
VREF+ (for DAC1/2): external voltage reference for DAC1 and DAC2 must be provided externally through VREF+.
 Duplicate DSP TMS320F28055PNT Microcontroller Binary
Duplicate DSP TMS320F28055PNT Microcontroller Binary
Duplicate DSP TMS320F28055PNT Microcontroller Binary from embedded flash memory, crack tamper resistance system of mcu tms320f28055 security fuse bit, copy the firmware from tms320f28055 flash memory to new MCU;
To designate the stages in the product development cycle, TI assigns prefixes to the part numbers of all TMS320™ MCU devices and support tools. Each TMS320 MCU commercial family member has one of three prefixes: TMX, TMP, or TMS (for example, TMS320F28069).
Texas Instruments recommends two of three possible prefix designators for its support tools: TMDX and TMDS. These prefixes represent evolutionary stages of product development from engineering prototypes (with TMX for devices and TMDX for tools) to fully qualified production devices/tools (with TMS for devices and TMDS for tools).
Device development evolutionary flow:
TMX Experimental device that is not necessarily representative of the final device’s electrical specifications when break tms320f28063 microcontroller flash memory protection;
TMP Final silicon die that conforms to the device’s electrical specifications but has not completed quality and reliability verification
TMS Fully qualified production device Support tool development evolutionary flow:
TMDX Development-support product that has not yet completed Texas Instruments internal qualification testing in order to restore dsp tms320f28067 microcontroller locked program;
TMDS Fully qualified development-support product
 Reverse Engineering Texas Instrument TMS320F28054PNQ Flash Memory
Reverse Engineering Texas Instrument TMS320F28054PNQ Flash Memory
Reverse Engineering Texas Instrument TMS320F28054PNQ Flash Memory can help to locate the security fuse bit of MCU and crack dsp microcontroller tms320f28054 tamper resistance, and then extract embedded heximal from tms320f28054 flash memory;
The TI Reference Design Library is a robust reference design library spanning analog, embedded processor, and connectivity. Created by TI experts to help you jump start your system design, all reference designs include schematic or block diagrams, BOMs, and design files to speed your time to market. Search and download designs at the Select TI reference designs page.
Digitally Controlled Non-Isolated DC/DC Buck Converter Reference Design
This design implements a non-isolated DC/DC buck converter that is digitally controlled using a C2000 microcontroller. The main purpose of this design is to evaluate the powerSUITE Digital Power Software tools in the process of reversing secured dsp cpu tms320f28051 memory. The design consists of two separate boards: 1) Digital Power BoosterPack™ Plug-in Module and
2) C2000 F28069M LaunchPad™ Development Kit or C2000 F28377S LaunchPad Development Kit.
672W Highly Integrated Reference Design for Automotive Bidirectional 48V-12V Converter Today’s automotive power consumption is 3KW, which will increase to 10KW in the next 5 years.
A 12-V battery is unable to provide that much power. The 48-12V bidirectional convertor provides a high-power requirement solution with two phases, each capable of running 28 A. This solution allows bidirectional current control of both phases using a C2000 control stick and firmware OCP and OVP in order to attack dsp controller tms320f28053 flash memory.
The 48-12V bidirectional converter removes the voltage conditioner need and distributes loads more evenly. The 48-V battery is used to power high-torque motors and other high-power components, such as A/C compressors and EPS, with no change to 12-V battery loads.
 Decode ST CPU ST72F321R9 Processor Locked Memory File
Decode ST CPU ST72F321R9 Processor Locked Memory File
Decode ST CPU ST72F321R9 Processor Locked Memory File needs to use laser cutting to remove the security fuse bit of microcontroller, and then copy embedded flash firmware from mcu st72f321r9;

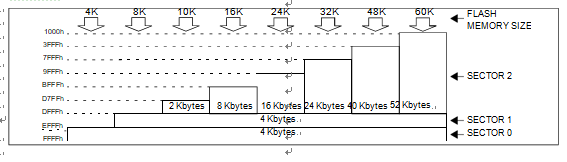
The Flash memory is organised in sectors and can be used for both code and data storage.
Depending on the overall Flash memory size in the micro-controller device, there are up to three user sectors (see below Table). Each of these sectors can be erased independently to avoid unnecessary erasing of the whole Flash memory when only a partial erasing is required after breaking st72f32ak1 mcu flash memory protection.
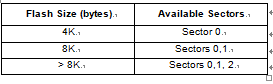
The first two sectors have a fixed size of 4 Kbytes (see below Figure). They are mapped in the upper part of the ST7 addressing space so the reset and in- terrupt vectors are located in Sector 0 (F000h- FFFFh).
3.5.1 Power supply schemes
- VDD = 2.4 to 3.6 V: external power supply for I/Os and the internal regulator. Provided externally through VDD pins.
- VDDA = from VDD to 3.6 V: external analog power supply for ADC, Reset blocks, RCs and PLL. The VDDA voltage level must be always greater or equal to the VDD voltage level and must be provided first.
 Decrypt ST72F321BK MCU Flash Memory Program
Decrypt ST72F321BK MCU Flash Memory Program
Decrypt ST72F321BK MCU Flash Memory Program is a process to pull the embedded firmware from st72f321bk mcu flash memory and then copy the heximal to new microcontroller;
The ST7 dual voltage High Density Flash (HDFlash) is a non-volatile memory that can be electrically erased as a single block or by individu- al sectors and programmed on a Byte-by-Byte ba- sis using an external VPP supply.
The HDFlash devices can be programmed and erased off-board (plugged in a programming tool) or on-board using ICP (In-Circuit Programming) or IAP (In-Application Programming) which can be applied for breaking mcu st72f321j9 flash memory.
The array matrix organisation allows each sector to be erased and reprogrammed without affecting other sectors.
- Three Flash programming modes:
- Insertion in a programming tool. In this mode, all sectors including option bytes can be pro- grammed or erased.
- ICP (In-Circuit Programming). In this mode, all sectors including option bytes can be pro- grammed or erased without removing the de- vice from the application board.
- IAP (In-Application Programming) In this mode, all sectors except Sector 0, can be pro- grammed or erased without removing the de- vice from the application board and while the application is running.
- ICT (In-Circuit Testing) for downloading and executing user application test patterns in RAM when attacking st72f321ar mcu protected flash memory
- Read-out protection
- Register Access Security System (RASS) to prevent accidental programming or erasing
 Attack STMicro ST72F321AR IC Chip Secured Memory
Attack STMicro ST72F321AR IC Chip Secured Memory
Attack STMicro ST72F321AR IC Chip Secured Memory and extract embedded MCU heximal file from flash memory, the firmware can be rewrite to new microprocessor st72f321ar for cloning;

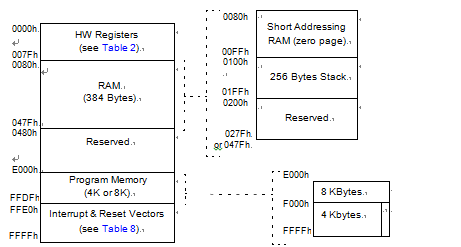
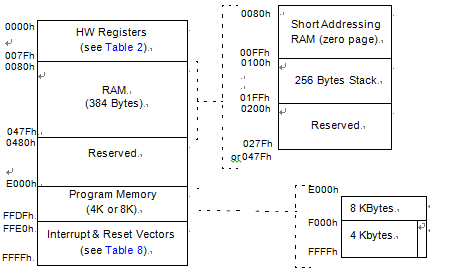
the MCU is capable of ad- dressing 64K bytes of memories and I/O registers.
The available memory locations consist of 128 bytes of register locations, up to 384 bytes of RAM and up to 8 Kbytes of user program memory. The RAM space includes up to 256 bytes for the stack from 0100h to 01FFh by reversing microcontroller st72f32aj1 microcontroller flash memory binary.
The highest address bytes contain the user reset and interrupt vectors.
IMPORTANT: Memory locations marked as “Re- served” must never be accessed. Accessing a re- served area can have unpredictable effects on the devices.
The contents of the I/O port DR registers are readable only in output configuration. In input configuration, the values of the I/O pins are returned instead of the DR register contents after breaking st72f321aj mcu flash memory fuse bit.
The bits associated with unavailable pins must always keep their reset value.
 Break ST72F321J9 Microcontroller Flash/ROM Memory
Break ST72F321J9 Microcontroller Flash/ROM Memory
Break ST72F321J9 Microcontroller Flash/ROM Memory and extract embedded data from secured flash controlled by microprocessor ST72F321J9, and then crack secured mcu st72f321j9 security fuse bit;
PIN DESCRIPTION (Cont’d)
For external pin connection guidelines, refer to See “ELECTRICAL CHARACTERISTICS” on page 113.
Legend / Abbreviations for Table 1:
Type: I = input, O = output, S = supply
Input level: A = Dedicated analog input In/Output level: C = CMOS 0.3VDD/0.7VDD
CT= CMOS 0.3VDD/0.7VDD with input trigger Output level:
HS = 20mA high sink (on N-buffer only)
Port and control configuration:
- Input:
- float = floating, wpu = weak pull-up, int = interrupt 1), ana = analog ports
- Output: OD = open drain 2), PP = push-pull
Refer to “I/O PORTS” on page 42 for more details on the software configuration of the I/O ports.
The RESET configuration of each pin is shown in bold. This configuration is valid as long as the device is in reset state.
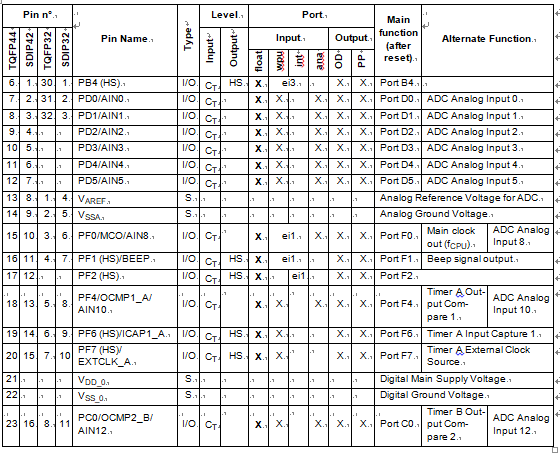
- In the interrupt input column, “eiX” defines the associated external interrupt vector. If the weak pull-up column (wpu) is merged with the interrupt column (int) when breaking st72f32ak1 microcontroller flash memory, then the I/O configuration is pull-up interrupt input, else the configuration is floating interrupt input.
- In the open drain output column, “T” defines a true open drain I/O (P-Buffer and protection diode to VDD are not implemented). See See “I/O PORTS” on page 42. and Section 12.8 I/O PORT PIN CHARACTER- ISTICS for more details.
- OSC1 and OSC2 pins connect a crystal/ceramic resonator, or an external source to the on-chip oscil- lator; see Section 1 INTRODUCTION and Section 12.5 CLOCK AND TIMING CHARACTERISTICS for more details.
- On the chip, each I/O port has 8 pads. Pads that are not bonded to external pins are in input pull-up configuration after reset and restore st72f32ak2 mcu encrypted flash heximal. The configuration of these pads must be kept at reset state to avoid added current consumption.
 Reverse ST ST72F32AJ1 Microcontroller Flash Memory Binary
Reverse ST ST72F32AJ1 Microcontroller Flash Memory Binary
Reverse ST ST72F32AJ1 Microcontroller Flash Memory Binary needs to crack secured mcu st72f32aj1 flash memory fuse bit over the protection and copy embedded firmware from st72f32aj1 microprocessor;
As shown in below Figure, the MCU is capable of ad- dressing 64K bytes of memories and I/O registers. The available memory locations consist of 128 bytes of register locations, up to 384 bytes of RAM and up to 8 Kbytes of user program memory by breaking st32f32ak1 mcu flash memory protection. The RAM space includes up to 256 bytes for the stack from 0100h to 01FFh.
The highest address bytes contain the user reset and interrupt vectors.
IMPORTANT: Memory locations marked as “Re- served” must never be accessed. Accessing a re- served area can have unpredictable effects on the device.
The contents of the I/O port DR registers are readable only in output configuration. In input configura- tion, the values of the I/O pins are returned instead of the DR register contents. The bits associated with unavailable pins must always keep their reset value.
 Restore ST Microcontroller ST72F32AK2 Encrypted Flash Heximal
Restore ST Microcontroller ST72F32AK2 Encrypted Flash Heximal
Restore ST Microcontroller ST72F32AK2 Encrypted Flash Heximal from embedded flash memory, unlock st72f32ak2 mcu fuse bit protection over its flash memory, then extract heximal file from microprocessor st72f32ak2 locked flash memory;
The ST72F32A and ST7232A devices are mem- bers of the ST7 microcontroller family designed for the 5V operating range.
The 32 and 44-pin devices are designed for mid- range applications All devices are based on a common industry- standard 8-bit core, featuring an enhanced instruc- tion set and are available with FLASH or ROM pro- gram memory.
Under software control, all devices can be placed in WAIT, SLOW, ACTIVE-HALT or HALT mode which can be used for breaking st72f32ak1 mcu flash memory protection;
Reducing power consumption when the application is in idle or stand-by state. The enhanced instruction set and addressing modes of the ST7 offer both power and flexibility to software developers, enabling the design of highly efficient and compact application code.
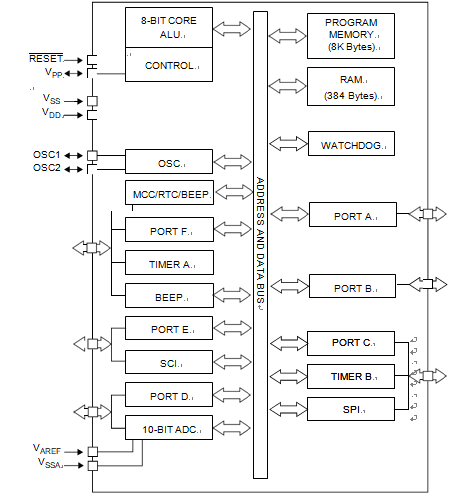
In addition to standard 8-bit data management, all ST7 micro- controllers feature true bit manipulation, 8×8 un- signed multiplication and indirect addressing modes.
 Break STMicrocontroller ST72F32AK1 Flash Memory Protection
Break STMicrocontroller ST72F32AK1 Flash Memory Protection
Break STMicrocontroller ST72F32AK1 Flash Memory Protection needs to remove the fuse bit of mcu embedded system and readout the locked memory firmware from processor;
8K dual voltage High Density Flash (HDFlash) or ROM with read-out protection capability. In- Application Programming and In-Circuit Pro- gramming for HDFlash devices
384 bytes RAM
HDFlash endurance: 100 cycles, data reten- tion: 40 years at 85°C
■ Clock, Reset And Supply Management
Clock sources: crystal/ceramic resonator os- cillators and bypass for external clock
PLL for 2x frequency multiplication
Four Power Saving Modes: Halt, Active-Halt, Wait and Slow
■ Interrupt Management
Nested interrupt controller
14 interrupt vectors plus TRAP and RESET
6 external interrupt lines (on 4 vectors)
■ Up to 32 I/O Ports
32/24 multifunctional bidirectional I/O lines
22/17 alternate function lines
12/10 high sink outputs
■ 4Timers
Main Clock Controller with: Real time base, Beep and Clock-out capabilities
Configurable watchdog timer in order to break stm8s207k6 locked mcu memory
Two 16-bit Timers with: 2 input captures, 2 output compares, PWM and pulse generator modes
■ 2 Communications Interfaces
SPI synchronous serial interface
SCI asynchronous serial interface
– 10-bit ADC with up to 12 robust input ports
■ Instruction Set
8-bit Data Manipulation
63 Basic Instructions when recover secured stm8s207c6 microcontroller heximal file
17 main Addressing Modes
8 x 8 Unsigned Multiply Instruction
■ Development Tools
Full hardware/software development package
In-Circuit Testing capability